Key Takeaways
- CNC plasma cutting machines use computer-controlled plasma torches to deliver precise and fast metal cutting, making them essential in modern fabrication industries.
- These machines are versatile, cutting various conductive metals like steel, aluminum, and copper, while offering high repeatability and minimal manual intervention.
- System types range from manual and portable units to automated table systems, supporting both low-volume custom work and large-scale production.
- Key benefits include rapid cutting speeds, tight tolerances (as fine as ±0.25 mm), low operational costs, and the ability to produce complex shapes.
- Limitations involve edge quality variance on thicker metals, production of noise and fumes, restricted use to conductive materials, and higher startup costs compared to traditional cutting tools.
- CNC plasma cutting is widely used across automotive, aerospace, construction, and custom manufacturing for its efficiency, adaptability, and consistent results.
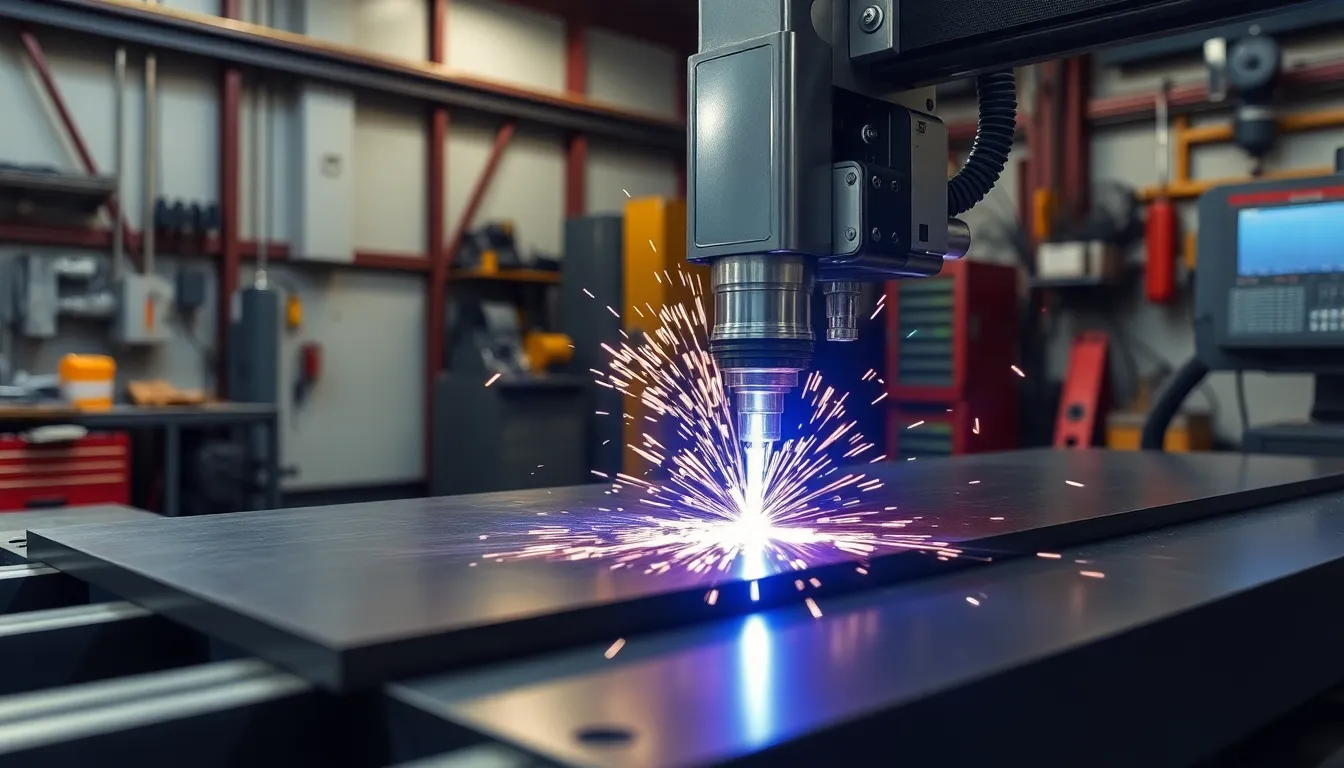
CNC plasma cutting machines utilise computer-controlled plasma torches to deliver precise and rapid metal cutting through high-temperature ionised gas exceeding 20,000°C. These advanced systems cut various conductive metals including steel, aluminium, and copper with tolerances as fine as ±0.25mm, making them essential for modern fabrication industries. Companies like Yijin Hardware leverage this technology to support precision manufacturing across automotive, aerospace, and energy sectors with consistent, repeatable results.
What Is CNC Plasma Cutting Machine?
CNC plasma cutting machine refers to a computer-controlled system equipped with a plasma torch that cuts metals with high precision. The process uses electrically ionized gas, generating temperatures exceeding 20,000°C to melt conductive metals like steel, aluminum, and copper. Software controls the torch head, enabling automated movements along designated paths. CNC plasma equipment delivers accurate cuts for flat and shaped metal parts, supporting cut tolerances as fine as ±0.25 mm on thin materials.
Manufacturers install CNC plasma cutters in production shops that need consistent quality and repeatable shapes. Fabricators use these machines for sheet metal processing and custom parts fabrication. The system relies on digital files for precise design input, minimizing manual intervention and operator error. Automated nesting features optimize material usage and reduce waste.
In the US manufacturing sector, CNC plasma cutting technology offers speed, accuracy, and adaptability for small batches and larger production runs. System sizes range from small desktop units to large industrial platforms over 10 feet in length. Safety features include enclosed torch assemblies and integrated exhaust extraction for fume control.
Yijin Hardware, located in Homestead, FL, utilizes CNC plasma cutting to support its range of precision manufacturing services. The company integrates this technology for custom hardware, sheet metal components, and complex assemblies, serving clients in automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy sectors.
How CNC Plasma Cutting Machines Work
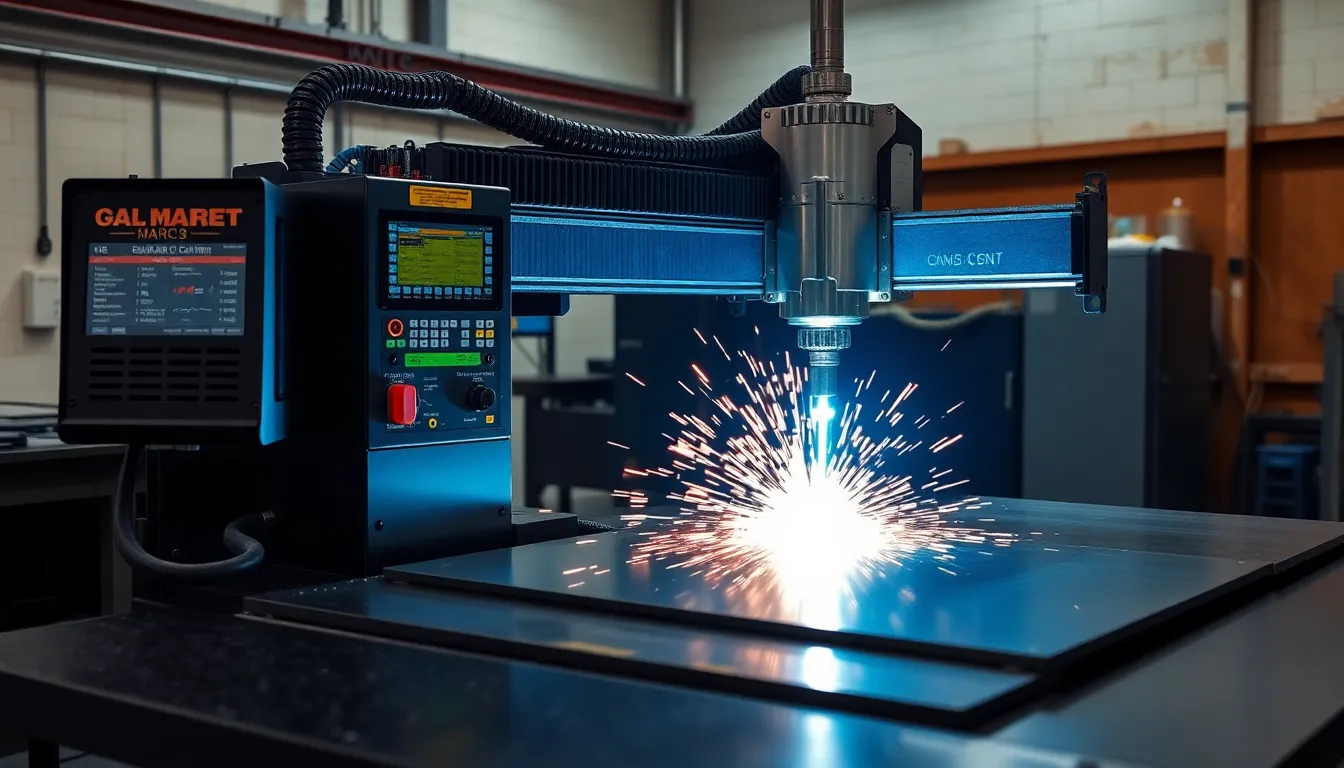
CNC plasma cutting machines use digital instructions to control a high-temperature plasma arc, producing clean cuts in conductive metals. Shops use this process when projects demand precision, speed, and repeatability for components.
Key Components of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
CNC plasma cutting machines contain core parts designed for performance and consistency:
- CNC Controller: Receives CAD or CAM files and guides the torch path with high accuracy.
- Plasma Torch: Generates an ionized gas stream reaching over 20,000°C, cutting metals such as steel and aluminum.
- Power Supply: Supplies consistent energy for arc formation and stable cutting performance.
- Gas Delivery System: Provides compressed air or gases (examples: oxygen, nitrogen) to suit application needs.
- Worktable: Secures materials and often integrates fume extraction for operator safety.
- Motion System: Employs rails and stepper motors for precise multi-axis movement.
Yijin Hardware in Homestead, FL configures each machine based on material thickness, cut shapes, and customer specifications to ensure optimal throughput.
The Plasma Cutting Process Explained
The plasma cutting process uses automated controls and thermal energy to separate metal efficiently:
- Digital file upload: Operators load part drawings directly to the CNC controller, eliminating manual layout.
- Torch ignition: The plasma torch initiates an electric arc, ionizing a chosen gas into plasma.
- Material penetration: High-velocity plasma melts the metal along the programmed toolpath, producing a kerf as narrow as 1.2 mm.
- Motion control: The CNC system moves the torch according to the digital pattern, maintaining tolerances of ±0.25 mm.
- Edge quality management: Automated height sensors and speed adjustments maintain consistent cut quality across thick or thin materials.
Yijin Hardware uses this method for short runs and production batches, serving automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy industries with minimized scrap and high repeatability.
Types of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
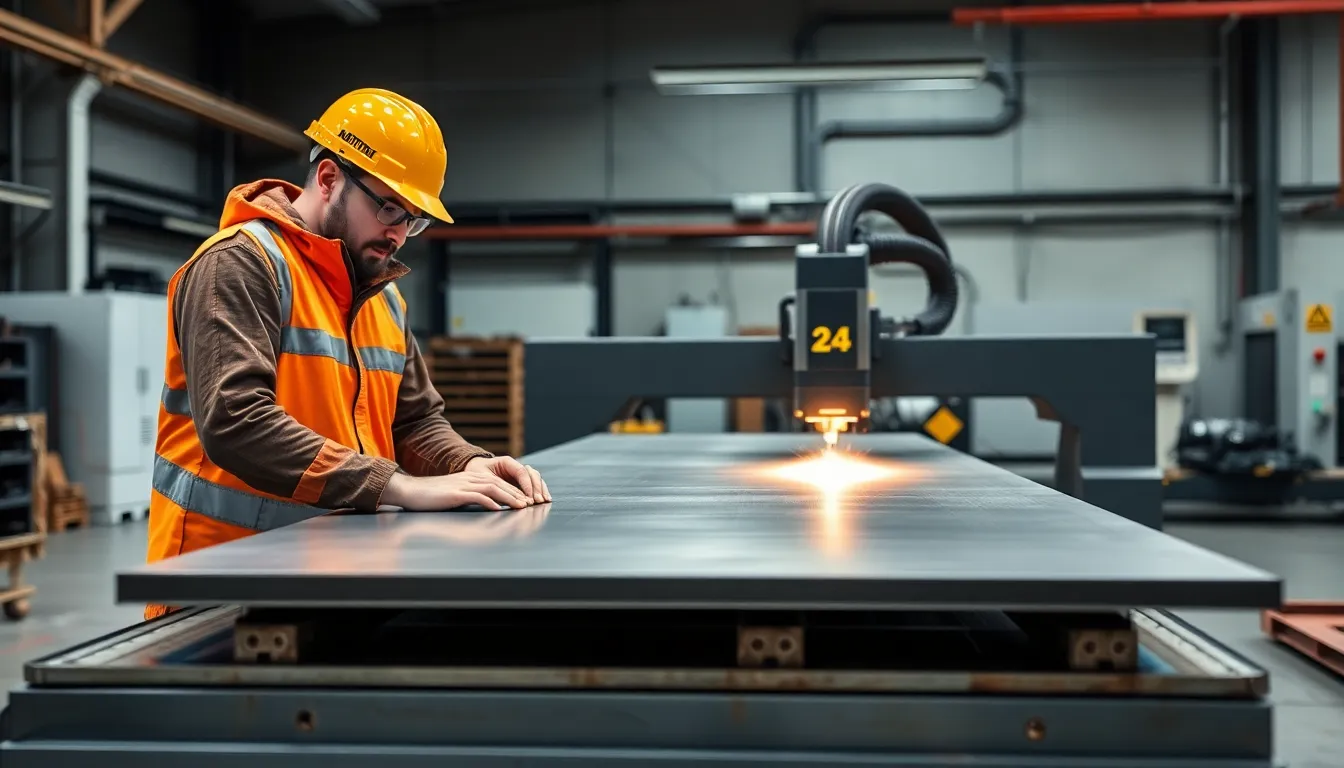

CNC plasma cutting machines operate in several formats, each suited for distinct fabrication needs. System configuration and mobility determine the capabilities of each type.
Manual vs. Automated Plasma Cutters
Manual plasma cutters rely on direct operator control, with the user guiding the torch over the metal using hand motions. These units are common in repair shops and fieldwork for small-scale tasks, adjustments, and maintenance. Automated CNC plasma cutters use computer programming to direct cutting paths, enabling precise, repeatable shapes on flat or contoured metals. Systems integrate software-driven motion, reducing human error and enhancing output quality. Automated models, with programmable accuracy, dominate environments where tight tolerances and high-volume parts are required, such as Yijin Hardware’s facility. Automated cutters optimize time and material efficiency in automotive and aerospace production.
Table vs. Portable CNC Plasma Machines
Table CNC plasma machines feature fixed beds, providing stable support for metal sheets and accurate positioning for automated cutting. Yijin Hardware operates fixed-table systems in Homestead, FL, leveraging their rigidity for consistent production of OEM components. Stations handle thick or large panels, integrating safety and fume extraction. Portable CNC plasma machines deliver flexibility, with lighter frames and transportable gantries. Fabricators use these for onsite installation, repair, or construction, when moving large panels isn’t practical. Portable units often include computer control on a compact frame, supporting smaller runs or field fabrication, with reduced setup but less precision than table models.
Advantages and Limitations of CNC Plasma Cutting
CNC plasma cutting offers industrial users speed, flexibility, and accuracy in processing metal parts. Each benefit enables higher productivity, but users must also account for several trade-offs and limitations during project planning.
Major Benefits in Industrial Applications
- High Cutting Speed
CNC plasma cutting machines process mild steel up to 25 mm at speeds between 1,000–2,000 mm/min, which accelerates cycle times in fabrication shops.
- Precision and Repeatability
Systems achieve tolerance levels as tight as ±0.25 mm, supporting applications in sectors such as aerospace and medical equipment manufacturing.
- Material Versatility
These machines cut conductive metals, including steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, improving workload adaptability for production facilities.
- Low Operational Costs
Automated operation reduces labor requirements and material waste, especially when used with nesting software for optimized sheet layouts.
- Complex Shape Capability
The CNC controller generates intricate geometries from CAD files, supporting projects that demand custom profiles and frequent design changes.
- Fast Setup and Changeover
Shops like Yijin Hardware in Homestead, FL, quickly adapt to new orders due to digital programming, which requires minimal mechanical adjustment.
Common Drawbacks to Consider
- Edge Quality Variance
Thicker metal sections above 30 mm may exhibit more dross and less uniform cut quality compared to laser or waterjet systems.
- Heat-Affected Zone
Plasma cutting induces localized high temperatures, potentially altering metallurgy or causing warping on thin or sensitive materials.
- Material Limitations
Non-conductive materials such as plastics or glass can’t be cut, restricting processing scope to metals only.
- Noise and Fume Generation
Operations produce high noise levels over 85 dB and generate fumes containing fine particulates, requiring industrial ventilation and hearing protection.
- Initial Investment for Automation
CNC plasma systems’ price ranges from $10,000 to over $150,000 depending on bed size and power, which may not fit smaller production budgets.
- Precision Cap Limits
Dimensional accuracy is generally lower than high-end laser cutters, making it less suited for ultra-fine tolerance projects in microelectronics.
| Benefit or Limitation | Specifics |
|---|---|
| High Cutting Speed | Up to 2,000 mm/min on mild steel under 25 mm |
| Precision & Repeatable | Tolerances to ±0.25 mm |
| Material Versatility | Cuts steel, stainless, aluminum |
| Low Operational Costs | Reduces labor; improves material usage |
| Shape Complexity | Supports intricate patterns from digital files |
| Fast Setup | Quick changeovers at shops like Yijin Hardware |
| Edge Quality Limits | Dross/roughness above 30 mm thickness |
| Heat-Affected Zone | Alters thin metals’ properties |
| Limited Materials | Metals only, not plastics/glass |
| Noise/Fume | >85 dB noise, industrial ventilation needed |
| Startup Cost | $10,000–$150,000+ system cost |
| Precision Limit | Lower than laser/waterjet for micro-features |
Comparing CNC Plasma Cutting with Other Cutting Methods
CNC plasma cutting competes with oxy-fuel cutting, laser cutting, and waterjet cutting in metal fabrication. CNC plasma matches oxy-fuel on mild steel up to 50 mm but outpaces it in speed for thinner metals; plasma machines cut at 500 mm/min for 12 mm mild steel, while oxy-fuel averages 125 mm/min (Hypertherm, 2022). CNC plasma provides faster cycle times and reduced heat input, though it can’t cut non-conductive materials unlike waterjet and laser systems.
Laser cutting achieves higher tolerances, ±0.05 mm for thin metals, which exceeds CNC plasma’s ±0.25 mm. However, laser machines cost over $250,000 new, which is about 4x a CNC plasma unit’s cost at similar table size (Fabricating and Metalworking, 2023). Waterjet cutting processes both metals and nonmetals like glass or rubber but operates slower, with cutting speeds for 12 mm steel averaging 50 mm/min.
Users at Yijin Hardware choose CNC plasma for automotive chassis, structural steel assemblies, and energy sector brackets due to speed and cost-effectiveness. For aerospace components or thin-gauge parts, the team selects laser or waterjet methods to achieve tighter tolerances or to process heat-sensitive alloys. Gavin Yi, CEO, confirms plasma’s advantage for rapid production of large steel profiles, supporting mass fabrication clients in Homestead, FL and nationwide.
| Cutting Method | Average Tolerance (mm) | Max Cut Thickness (mm) | Speed (12 mm Mild Steel, mm/min) | Startup Cost (USD) | Material Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Plasma | ±0.25 | 50 | 500 | $60,000–$80,000 | Conductive metals |
| Laser | ±0.05 | 20 | 200 | $250,000+ | Metals, some plastics, thin sheets |
| Oxy-fuel | ±0.50 | 150 | 125 | $10,000–$50,000 | Mild steel only |
| Waterjet | ±0.10 | 200 | 50 | $120,000–$200,000 | Metals, nonmetals, composites |
Applications of CNC Plasma Cutting Machines
CNC plasma cutting machines handle metal fabrication tasks in sectors like automotive, aerospace, construction, shipbuilding, and custom manufacturing. Manufacturers cut automotive chassis parts, brackets, and frame components. Aerospace fabricators use plasma systems for airframe sections, mounting plates, and support structures according to design files. Construction firms cut structural beams, columns, and base plates for on-site assembly. Shipyards fabricate hull sections, decks, and bulkheads using plasma technology.
Industrial shops perform artistic metalwork, including custom signage, decorative panels, and prototypes. Maintenance teams repair heavy equipment parts—buckets, blades, and gussets. Product developers at Yijin Hardware in Homestead, FL, apply CNC plasma cutting for both low-volume prototypes and high-volume orders. Their projects cover precision components for medical devices, energy sector enclosures, and aerospace brackets.
Job shops rely on CNC plasma machines for fast turnaround on one-off parts and small batches. OEMs select table-based systems for repeatable, high-accuracy production runs. Businesses using Yijin Hardware’s CNC plasma capabilities receive consistent results, reduced material waste, and support for complex geometries across multiple industries.
About Yijin Hardware
Yijin Hardware, located in Homestead, FL, is a leading provider of precision manufacturing services.
Led by CEO Gavin Yi, Yijin Hardware offers a range of services including CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and custom fasteners. The company also provides additional solutions such as die casting, injection molding, and 3D printing, supporting industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and energy. With a commitment to high-quality and reliable manufacturing, Yijin Hardware delivers tailored solutions to meet the unique needs of each client.
Contact:
Gavin Yi, CEO
Phone: +1 626 263 5841
Email: [email protected]
Address: 760 NW 10th Ave, Homestead, FL 33030
Website: www.yijinsolution.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a CNC plasma cutting machine?
A CNC plasma cutting machine is an automated system that uses a computer-controlled plasma torch to cut metal with high precision. It utilizes electrically ionized gas to generate extremely high temperatures, allowing it to cut through various metal types cleanly and accurately.
How does CNC plasma cutting work?
CNC plasma cutting works by following digital files to guide a plasma torch, which emits a high-temperature jet to melt and cut metal. The process is automated by a CNC controller, ensuring consistent, repeatable results with minimal manual intervention.
What materials can CNC plasma cutters process?
CNC plasma cutters are primarily designed for conductive metals like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. They cannot cut non-conductive materials such as glass, plastic, or wood.
What industries use CNC plasma cutting machines?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, shipbuilding, medical device manufacturing, and custom fabrication use CNC plasma cutting machines for their precision, speed, and versatility in cutting various metal parts.
What are the main advantages of CNC plasma cutting?
CNC plasma cutting offers high cutting speeds, excellent precision, versatility with different metals, low operational costs, the ability to handle complex shapes, and fast setup times, making it ideal for both small and large production runs.
What are the limitations of CNC plasma cutting?
Limitations include less edge quality on thicker materials, heat-affected zones, inability to cut non-conductive materials, noise and fume generation, higher initial costs, and lower precision compared to laser cutting on certain fine-detail work.
How does CNC plasma cutting compare to laser or waterjet cutting?
CNC plasma cutting is faster and more cost-effective for medium-thick metals but has a larger heat-affected zone and lower precision than laser or waterjet systems. Laser provides tighter tolerances, while waterjet can cut a wider range of materials, including nonmetals.
What types of CNC plasma cutting machines are available?
There are table-based machines, which offer stable, highly accurate cutting, and portable machines, which are more flexible for onsite work but typically provide less precision. Fully automated CNC systems are recommended for large production runs.
Is CNC plasma cutting suitable for both small and large production runs?
Yes, CNC plasma cutters are adaptable for both one-off parts and high-volume manufacturing. Fast setup and digital control allow for efficient production regardless of batch size.
What safety considerations are important with CNC plasma cutting?
Safety measures include proper ventilation, use of personal protective equipment, regular machine maintenance, and ensuring that only trained operators use the machine due to high temperatures, noise, and fume production during cutting.

